Radio links are traditionally required to be manually directed towards each other in order to communicate. This process of directing antennas is time consuming and requires specially trained staff, resulting in a costly installation. Further, traditional radio links limit data to be transferred between two specific nodes only, creating a so-called “Point-to-Point” communication.
Steerable antennas, on the other hand, enable radio links to be automatically aligned towards each other (see figure below). This results in an increased ease-of-use due to a simpler, cheaper and faster installation process. In addition, no further adjustments of the antennas are needed, which reduces the maintenance costs. Steerable antennas also enable one node to communicate with several other nodes, so-called “Point-to-Multi-Point” communication.
Point-to-Multi-Point communication enables the development of a so-called “mesh networks”, which make it possible to redirect the data traffic away from over-loaded base-stations and route the data where it can be processed faster. This will furthermore enable optimization of the processing capacity in the mobile data networks resulting in less congestion. Already today, congestions in the mobile data network is the key cause of interrupted data traffic, and it will be an even larger challenge in the future.
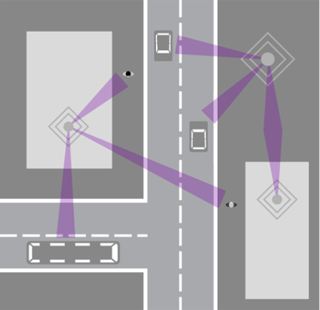 Antennas are automatically aligned towards each other and end users
Antennas are automatically aligned towards each other and end users
Steerable antennas also enable a directed connection to individual users, which increases the data transfer rate from mobile devices to base stations (see figure above). Ericsson demonstrated this at the 2016 Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, where they reached transfer rates at up to 25 Gbps (http://www.microwavejournal.com/articles/26090-mobile-world-congress-breaking-records). The build-out of the next generation of mobile data networks, 5G, requires millions of high performing antennas to be installed closer to the end users. Since steerable antennas enable higher data transfer rates at a lower installation cost, they are expected to be a key component in the development of 5G.


Opinions